Protists
-these are eukaryotes with nuclei and other membrane-bound organelles
-most of them are unicellular organisms, however, some of the protists are multicellular organisms, and few of them are very large
Algae
-plantlike protists that perform photosynthesis
-algae contain chlorophyll and produce glycogen as a by-product of photosynthesis
-many algae contain cellulose cell walls, just as plants do.
-they live whereever there is sufficient water. They grow in ponds, in salt water, in moist soil and even on the surface of the ice
-both plants and algae capture the energy of the sun through the photosynthesis and store it, making the energy usable to heterotrophs
-they provide food for other organisms, they also produce oxygen
Colonial organisms- are clusters, or colonies.
Unicellular Algae
-include the dinoflagellates, diatoms and euglenoids.
Dinoflagellates
Dinoflagellates are algae with two flagella that spin the cells through the water. Generally, the two flagella arise from two grooves and at right angles to one another . One flagellum circles the cell like a head and the other sticks out like a tail. The rhythmic beating of its flagella propel a dinoflagellate through the water like a spinning top. The majority of dinoflagellates grow in saltwater habitats. Others are free-living while some have symbiotic relationships with jellyfish, sea anemones, corals and other organisms hat live near the coral reefs. Symbiotic dinoflagellates supply nutrients to the animals which they live. Symbiotic dinoflagellates do not have a flagella.
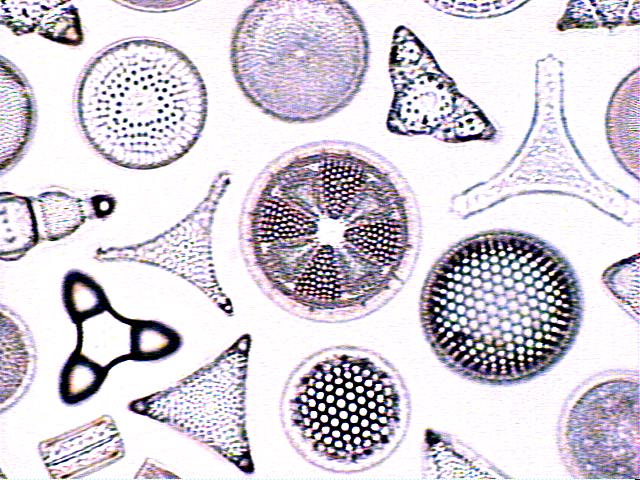
Diatoms
Diatoms are algae that lack both cilia and flagella and have glass walls containing silica. The cell walls of diatoms consist of two halves that fit together like a lid on Petri dish. Each diatom has a pair of pores that allows gases and other materials to pass through cell walls. There are many patterns of diatoms. Diatoms are among the most abundant organism in the Earth. Probably because they contain oil, diatoms float in the water. When diatoms die, their shells sink to the bottom of the sea. Soil deposits contanining shells are known diatomaceous Earth. Its tough, gritty-structures makes diatomaceous Earth deposits useful for products such as lotion, detergents, and cleaners and cleaners, abrasives, polishing agents and toothpaste.
Euglenoids
The Euglenoids are organisms similar to the organism Euglena. Euglenoid has no rigid cell wall. Instead, Euglena has a flexible protein covering called pellicle. Eulena has a flagella. They are difficult to classify because they are both algae and protozoa . Since many of them have chloroplasts and perform photosynthesis, in the past they were called as algae. They have flagella like some protozoans, they have pellicle like many ciliates. Euglenas that have grown in darkness lose theirchloroplastsand fuction as heterotrophs. Some scientists hink Euglenas should belong to protozoans.
Multicellular Algae
-Many algae have multicelled bodies.
-A body of a multicellular alga is called a thallus. A thallus can have many specialized structures including stringlike filaments and leaflike sheets, or rootlike holdfasts.
-Microbiologists have now classifid algae as protists because they have different reproductive structuresfom plants.
Green Algae
Green Algae ore Chlorophyta are green and multicellular. However some algae are unicellular and some are colonial. In stressful conditions Green Algaes contract their flagella and becomes dormant.When their is water present, they will regrow their flagella, increase their size and reproduces. After rainfall, algae that have been dormant grow in puddles and drainage ditches.
Volvox is a common colonial green algae. In Volvox, clusters of cells with flagella live together in a ball-shaped colony. The colonies may contain several thousand cell. Some cells are specialized for specific functions such as reproduction.
The multicellular green algae either grow as filaments, with cells hooked from end to end, or as flat, leaflike sheets of cells.
Most green algae live in fresh water and moist soil. A few green algae live symbiotic relationships with organisms such as Paramecium, Hydra and fungi. A symbiotic association between an alga and a fungus is called a lichen.


Red Algae
Most of the red algae or rhodophyta are muticellular organismsand grow mainly in saltwater habitats. Typically, red algae have a thalli with branched filaments and are less than 1m long. However, not all red algae are red. Besides chlorophyll, the red algae have other pigments that trap sunlight. Their accesory pigments allow the red algaeto use the light that penetrates into deep water for photosynthesis. Consequently, red algae can live where there is too little moist for most other plants and algae.
Coralline red algae are an important component of coral reefs. Coralline red algae have calcium carbonate in their cell walls. Besides cellulose, the coralline algae have calcium carbonate in their cell walls. Calcium carbonate makes the branching red algae stiff.
to be continued..



No comments:
Post a Comment